Effect of solvent hydrophobicity on gelation kinetics and phase diagram of gelatin ionogels†
Abstract
We present a systematic investigation of the effect of solvent hydrophobicity (alkyl chain length) on the gelation kinetics and the phase states of the polypeptide gelatin in imidazolium based ionic liquid (IL) solutions. We have observed that IL concentration and hydrophobicity had dramatic influences on the thermal and viscoelastic properties of gelatin ionogels. Gelation concentration cg was observed to increase from 1.75 to 2.75% (w/v) while the gelation temperature Tg was found to decrease from 32 to 26 °C with increase in 1-octyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride [C8mim][Cl] (most hydrophobic) concentration as compared to the case of the least hydrophobic IL 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium chloride [C2mim][Cl], where the corresponding changes were marginal. Gradual softening of the gel with increase in hydrophobicity and concentration of IL was clearly noticed. The viscosity of the gelling sol diverged as ηr ∼ ε−k1 and storage modulus of gel grew as G0 ∼ εt1 where ε1 = |1 − c/cg| with the exponents having values k = 1.2–1.8 ± 0.08 and t = 1.2–1.6 ± 0.08, close to but not exactly the same as predicted by the percolation model: k = 0.7–1.3 and t = 1.9. Thus, the gelation kinetics involved in the growth of interconnected networks could be conceived to follow an anomalous percolation model. The temporal growth of self-assembled structures followed a power law dependence given by: ηr ∼ ε−α2 and Rh ∼ ε−β2 where 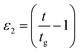 , t > tg (α = 1–2.9 ± 0.08 and β = 1–2.7 ± 0.08). The low frequency storage modulus G0, gelation temperature Tg, gelation concentration cg and gelation time tg adequately defined the sol–gel phase diagram. Results clearly revealed that by adjusting the hydrophobic chain length and concentration of IL it was possible to customize both thermal and mechanical properties of these ionogels to match specific application requirements.
, t > tg (α = 1–2.9 ± 0.08 and β = 1–2.7 ± 0.08). The low frequency storage modulus G0, gelation temperature Tg, gelation concentration cg and gelation time tg adequately defined the sol–gel phase diagram. Results clearly revealed that by adjusting the hydrophobic chain length and concentration of IL it was possible to customize both thermal and mechanical properties of these ionogels to match specific application requirements.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...