A kinetic model for ozone uptake by solutions and aqueous particles containing I− and Br−, including seawater and sea-salt aerosol†
Abstract
The heterogeneous interactions of gaseous ozone (O3) with seawater and with sea-salt aerosols are known to generate volatile halogen species, which, in turn, lead to further destruction of O3. Here, a kinetic model for the interaction of ozone (O3) with Br− and I− solutions and aqueous particles has been proposed that satisfactorily explains previous literature studies about this process. Apart from the aqueous-phase reactions X− + O3 (X = I, Br), the interaction also involves the surface reactions X− + O3 that occur via O3 adsorption on the aqueous surface. In single salt solutions and aerosols, the partial order in ozone and the total order of the surface reactions are one, but the apparent total order is second order because the number of ozone sites where reaction can occur is equal to the surficial concentration of X− ([X−]surf). In the presence of Cl−, the surface reactions are enhanced by a factor equal to 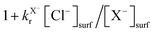 , where
, where 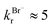 and
and 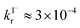 . Therefore, we have inferred that Cl− acts as a catalyst in the surface reactions X− + O3. The model has been applied to estimate ozone uptake by the reaction with these halides in/on seawater and in/on sea-salt aerosol, where it has been concluded that the Cl−-catalyzed surface reaction is important relative to total ozone uptake and should therefore be considered to model Y/YO (Y = I, Br, Cl) levels in the troposphere.
. Therefore, we have inferred that Cl− acts as a catalyst in the surface reactions X− + O3. The model has been applied to estimate ozone uptake by the reaction with these halides in/on seawater and in/on sea-salt aerosol, where it has been concluded that the Cl−-catalyzed surface reaction is important relative to total ozone uptake and should therefore be considered to model Y/YO (Y = I, Br, Cl) levels in the troposphere.

- This article is part of the themed collection: 2019 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...