Constructing ultrathin CoP nanomeshes by Er-doping for highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting†
Abstract
Exploring highly efficient non-noble-metal bifunctional catalysts for water electrolysis is vital for the commercial production of hydrogen. In this study, Er, Nd, Ce, La and Gd doped CoP materials have been prepared to study the effects of rare earth (RE) element doping on both the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), among which Er-doped CoP is found to be the best bifunctional catalyst. The Er doped CoP ultrathin nanomeshes (NMs) can be synthesized with a larger surface area (123.4 m2 g−1) and double-layer capacitance (143.1 mF cm−2) than pure CoP nanoplates, and therefore with more active sites. Benefiting from the ultrathin nanomesh morphology and electronic structure modification, the as-prepared Er-doped CoP NMs show superior electrocatalytic activity in alkaline medium, which require an overpotential of only 256 mV for the OER to afford a current density of 10 mA cm−2, obviously smaller than that of most reported non-noble metal catalysts. Additionally, the Er-doped CoP NMs also display a favorable catalytic performance for the HER in both acidic and alkaline media with an overpotential of 52 mV and 66 mV at 10 mA cm−2, respectively. The excellent bifunctional nature of Er-doped CoP NMs will make the electrolysis device more operational and cost-effective. The corresponding two-electrode electrolysis system needs a cell voltage of merely 1.58 V at 10 mA cm−2 in alkaline medium, and maintains stable electrolysis for 25 h, which compares favorably with previously reported bifunctional catalysts. The density functional theory (DFT) calculations indicated that the superior performance of such a catalyst resulted from the smaller overpotential and hydrogen adsorption energy 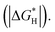 This study provides an appealing method to improve performance which can be extended to other transition metal catalysts.
This study provides an appealing method to improve performance which can be extended to other transition metal catalysts.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...