Space charge layer effect at the platinum anode/BaZr0.9Y0.1O3−δ electrolyte interface in proton ceramic fuel cells†
Abstract
The role and properties of interfaces are well understood in the field of semiconductors and aqueous electrochemistry, but less so in many cases of solid-state electrolytes. In this study, the interface between a solid-state proton conductor BaZr0.9Y0.1O3−δ (BZY10) and a metal phase (Pt), consisting of a positively charged core and an adjacent space charge layer (SCL) with opposite charges, was investigated for proton ceramic fuel cell (PCFC) applications. Considering the H2 oxidation reaction (HOR) at the Pt/BZY10 interface, the resistances of proton transport through the SCL (RSCL(H+)) and electron charge transfer (ECT) reactions (RECT) were identified using the distribution of relaxation time (DRT) analysis on the impedance spectra. The RSCL(H+) is shown to be independent on pH2 and sensitive to pH2O. And also, the positive dependency of 1/RECT with pH2O reveals a decrease of the electrical potential at the Pt/BZY10 interface (Δφ(x1)) with increasing pH2O. With the presence of a SCL, the exchange current density (j0) is a function of the anodic potential. As a result, the Tafel equation is modified based on the variable j0, giving an additional resistance (RSCLECT) with the expression of 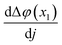 on top of the ideal RECT (absence of a SCL). At high positive bias (>0.2 V), a pronounced SCL effect on the kinetics of ECT reactions is estimated, with the ratio of RSCLECT/RECT being over 50%. This study is a first-time experimental investigation of the SCL effect at a metal/solid-state ionic conductor interface, demonstrated in the case of the HOR.
on top of the ideal RECT (absence of a SCL). At high positive bias (>0.2 V), a pronounced SCL effect on the kinetics of ECT reactions is estimated, with the ratio of RSCLECT/RECT being over 50%. This study is a first-time experimental investigation of the SCL effect at a metal/solid-state ionic conductor interface, demonstrated in the case of the HOR.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...