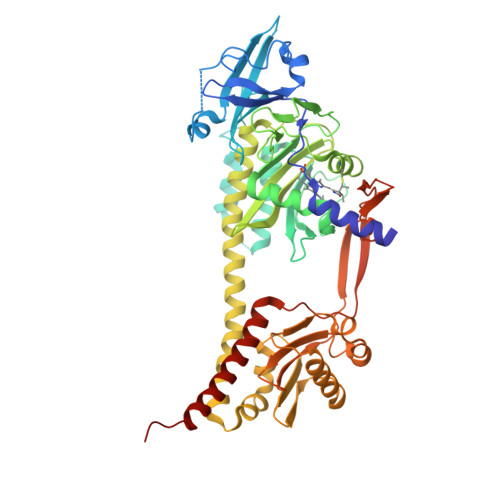
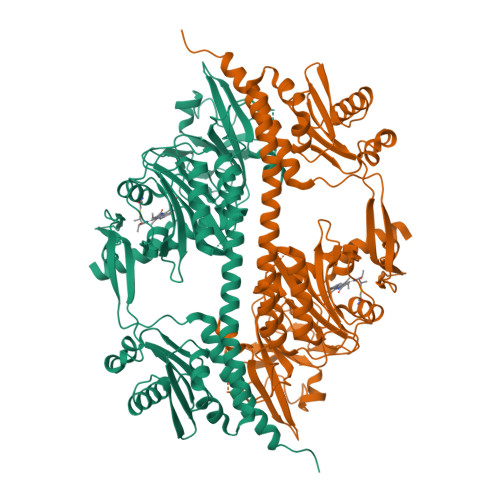
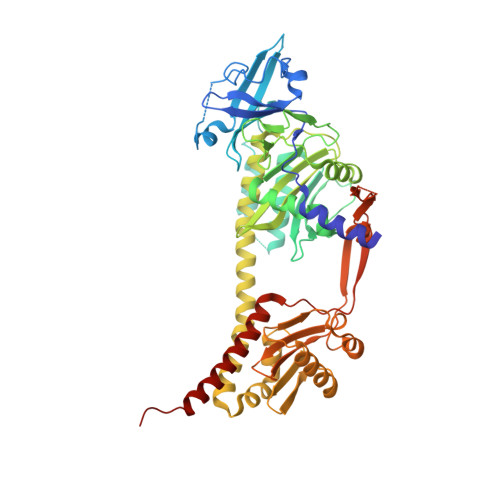
The Structure of a Complete Phytochrome Sensory Module in the Pr Ground State.
Essen, L.-O., Mailliet, J., Hughes, J.(2008) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: 14709
- PubMed: 18799745
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0806477105
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2VEA - PubMed Abstract:
Phytochromes are red/far-red photochromic biliprotein photoreceptors, which in plants regulate seed germination, stem extension, flowering time, and many other light effects. However, the structure/functional basis of the phytochrome photoswitch is still unclear. Here, we report the ground state structure of the complete sensory module of Cph1 phytochrome from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. Although the phycocyanobilin (PCB) chromophore is attached to Cys-259 as expected, paralleling the situation in plant phytochromes but contrasting to that in bacteriophytochromes, the ZZZssa conformation does not correspond to that expected from Raman spectroscopy. We show that the PHY domain, previously considered unique to phytochromes, is structurally a member of the GAF (cGMP phosphodiesterase/adenylyl cyclase/FhlA) family. Indeed, the tandem-GAF dumbbell revealed for phytochrome sensory modules is remarkably similar to the regulatory domains of cyclic nucleotide (cNMP) phosphodiesterases and adenylyl cyclases. A unique feature of the phytochrome structure is a long, tongue-like protrusion from the PHY domain that seals the chromophore pocket and stabilizes the photoactivated far-red-absorbing state (Pfr). The tongue carries a conserved PRxSF motif, from which an arginine finger points into the chromophore pocket close to ring D forming a salt bridge with a conserved aspartate residue. The structure that we present provides a framework for light-driven signal transmission in phytochromes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biochemistry, Department of Chemistry, Philipps University, Hans-Meerwein-Strasse, D-35032 Marburg, Germany. essen@chemie.uni-marburg.de