Non-nucleoside inhibitors of HCV polymerase NS5B. Part 4: structure-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of benzo[d]isothiazole-1,1-dioxides
de Vicente, J., Hendricks, R.T., Smith, D.B., Fell, J.B., Fischer, J., Spencer, S.R., Stengel, P.J., Mohr, P., Robinson, J.E., Blake, J.F., Hilgenkamp, R.K., Yee, C., Adjabeng, G., Elworthy, T.R., Li, J., Wang, B., Bamberg, J.T., Harris, S.F., Wong, A., Leveque, V.J., Najera, I., Le Pogam, S., Rajyaguru, S., Ao-Ieong, G., Alexandrova, L., Larrabee, S., Brandl, M., Briggs, A., Sukhtankar, S., Farrell, R.(2009) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19: 5652-5656
- PubMed: 19709881
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.08.022
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3H5S, 3H5U - PubMed Abstract:
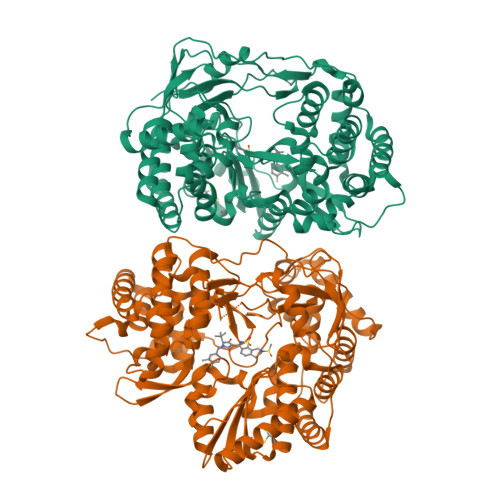
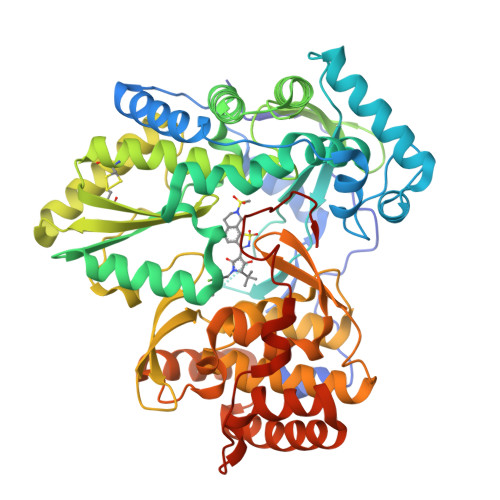
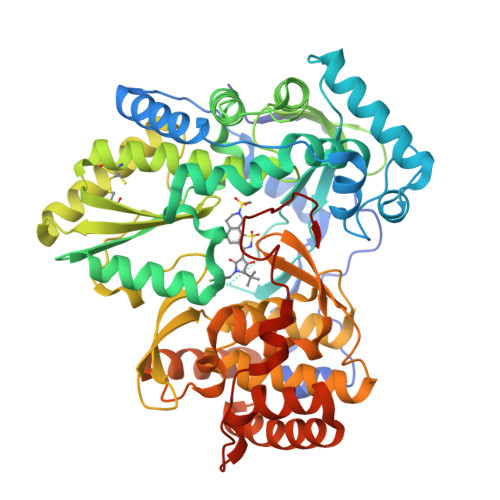
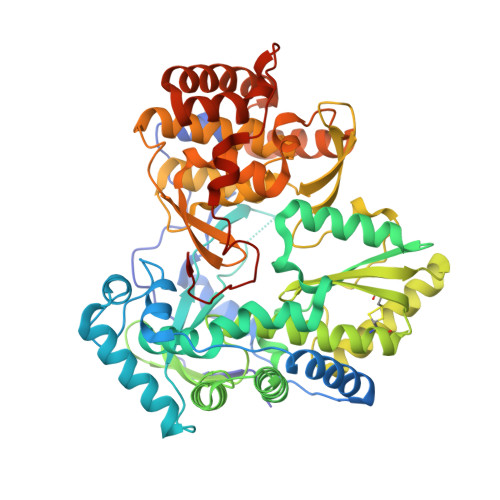
A series of benzo[d]isothiazole-1,1-dioxides were designed and evaluated as inhibitors of HCV polymerase NS5B. Structure-based design led to the incorporation of a high affinity methyl sulfonamide group. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies of this series revealed analogues with submicromolar potencies in the HCV replicon assay and moderate pharmacokinetic properties. SAR studies combined with structure based drug design focused on the sulfonamide region led to a novel and potent cyclic analogue.
Organizational Affiliation:
Roche Palo Alto LLC, 3431 Hillview Avenue, Palo Alto, CA 94304, USA. javier.devicente@roche.com