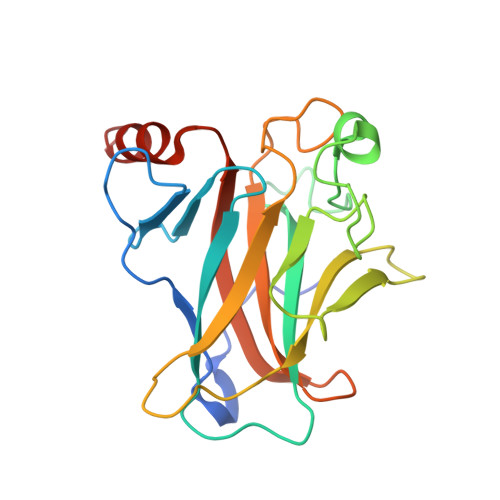
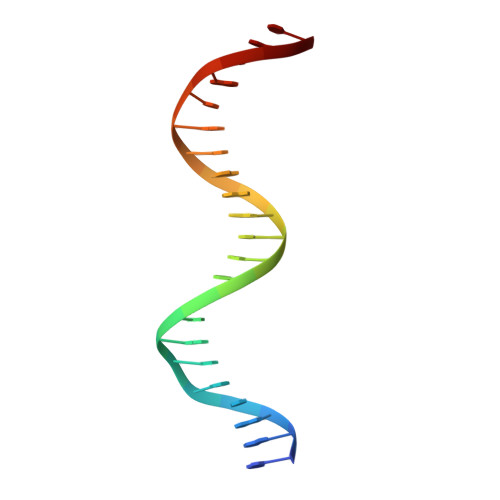
Pliable DNA Conformation of Response Elements Bound to Transcription Factor p63.
Chen, C., Gorlatova, N., Herzberg, O.(2012) J Biol Chem 287: 7477-7486
- PubMed: 22247550
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.315820
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3US0, 3US1, 3US2 - PubMed Abstract:
We show that changes in the nucleotide sequence alter the DNA conformation in the crystal structures of p63 DNA-binding domain (p63DBD) bound to its response element. The conformation of a 22-bp canonical response element containing an AT spacer between the two half-sites is unaltered compared with that containing a TA spacer, exhibiting superhelical trajectory. In contrast, a GC spacers abolishes the DNA superhelical trajectory and exhibits less bent DNA, suggesting that increased GC content accompanies increased double helix rigidity. A 19-bp DNA, representing an AT-rich response element with overlapping half-sites, maintains superhelical trajectory and reveals two interacting p63DBD dimers crossing one another at 120°. p63DBD binding assays to response elements of increasing length complement the structural studies. We propose that DNA deformation may affect promoter activity, that the ability of p63DBD to bind to superhelical DNA suggests that it is capable of binding to nucleosomes, and that overlapping response elements may provide a mechanism to distinguish between p63 and p53 promoters.
Organizational Affiliation:
W. M. Keck Laboratory for Structural Biology, Institute for Bioscience and Biotechnology Research and the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Maryland, Rockville, Maryland 20850, USA.