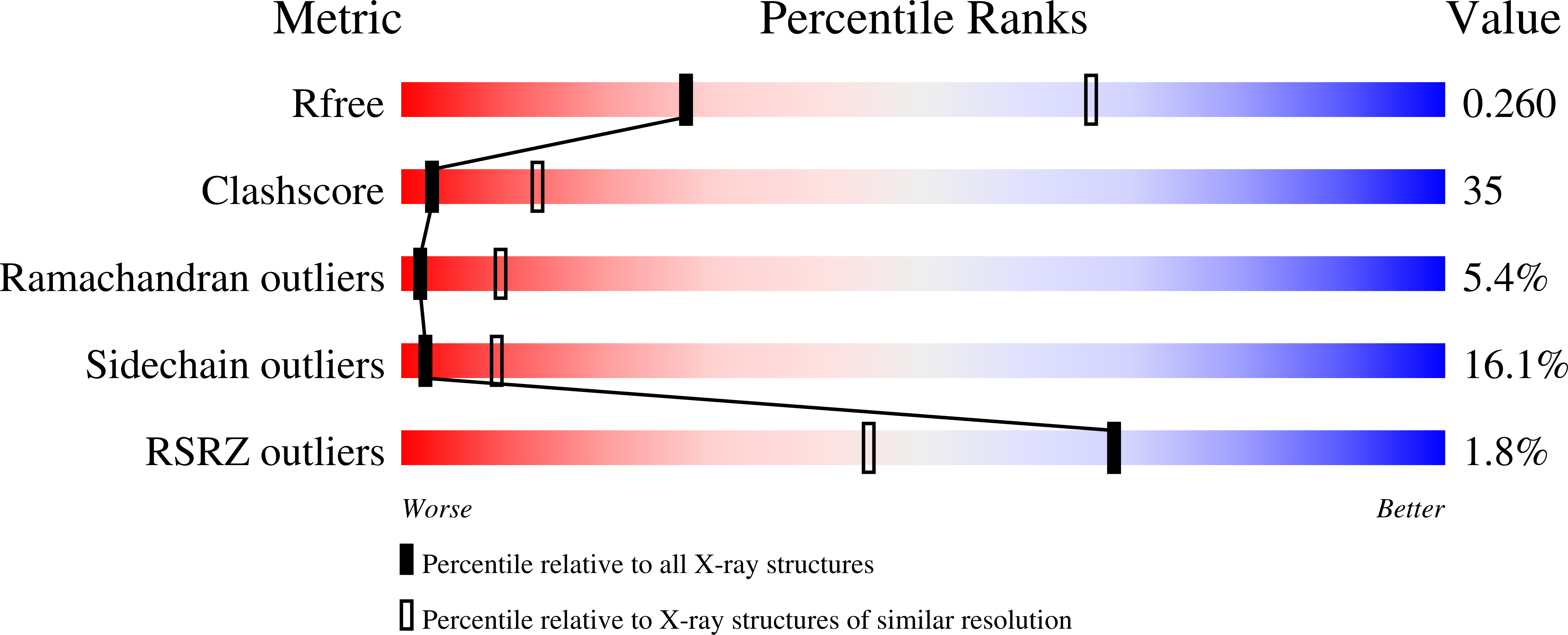
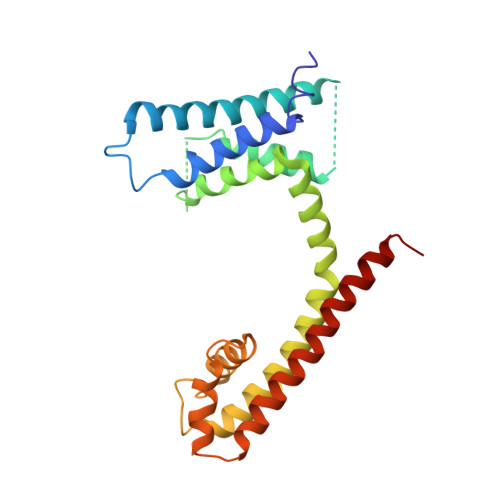
Crystal structure of an orthologue of the NaChBac voltage-gated sodium channel
Zhang, X., Ren, W.L., DeCaen, P., Yan, C.Y., Tao, X., Tang, L., Wang, J.J., Hasegawa, K., Kumasaka, T., He, J.H., Wang, J.W., Clapham, D.E., Yan, N.(2012) Nature 486: 130-134
- PubMed: 22678295
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11054
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DXW - PubMed Abstract:
Voltage-gated sodium (Na(v)) channels are essential for the rapid depolarization of nerve and muscle, and are important drug targets. Determination of the structures of Na(v) channels will shed light on ion channel mechanisms and facilitate potential clinical applications. A family of bacterial Na(v) channels, exemplified by the Na(+)-selective channel of bacteria (NaChBac), provides a useful model system for structure-function analysis. Here we report the crystal structure of Na(v)Rh, a NaChBac orthologue from the marine alphaproteobacterium HIMB114 (Rickettsiales sp. HIMB114; denoted Rh), at 3.05 Å resolution. The channel comprises an asymmetric tetramer. The carbonyl oxygen atoms of Thr 178 and Leu 179 constitute an inner site within the selectivity filter where a hydrated Ca(2+) resides in the crystal structure. The outer mouth of the Na(+) selectivity filter, defined by Ser 181 and Glu 183, is closed, as is the activation gate at the intracellular side of the pore. The voltage sensors adopt a depolarized conformation in which all the gating charges are exposed to the extracellular environment. We propose that Na(v)Rh is in an 'inactivated' conformation. Comparison of Na(v)Rh with Na(v)Ab reveals considerable conformational rearrangements that may underlie the electromechanical coupling mechanism of voltage-gated channels.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Bio-membrane and Membrane Biotechnology, Center for Structural Biology, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.