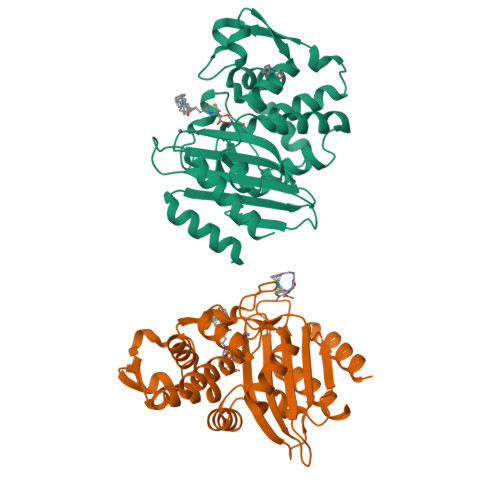
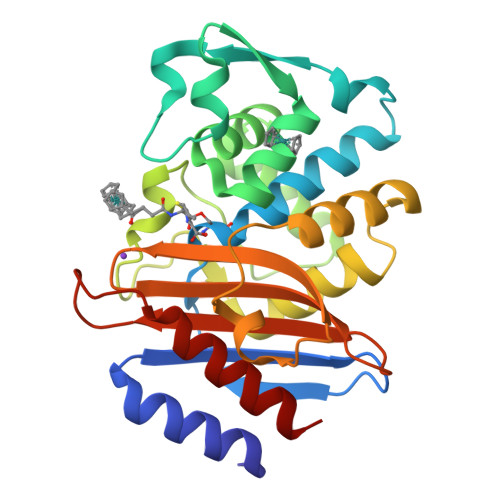
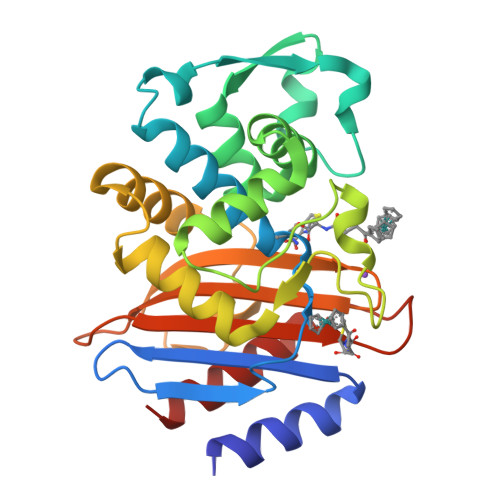
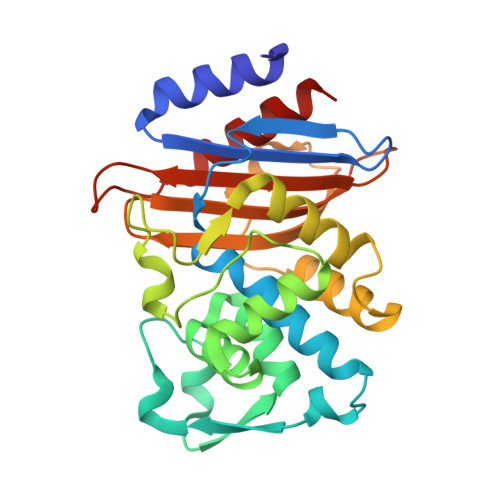
Antibacterial Properties of Metallocenyl-7-ADCA Derivatives and Structure in Complex with CTX-Mbeta-Lactamase.
Lewandowski, E.M., Szczupak, L., Wong, S., Skiba, J., Guspiel, A., Solecka, J., Vrcek, V., Kowalski, K., Chen, Y.(2017) Organometallics 36: 1673-1676
- PubMed: 29051683
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.organomet.6b00888
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5UJO - PubMed Abstract:
A series of six novel metallocenyl-7-ADCA (metallocenyl = ferrocenyl or ruthenocenyl; 7-ADCA = 7-aminodesacetoxycephalosporanic acid) conjugates were synthesized and their antibacterial properties evaluated by biochemical and microbiological assays. The ruthenocene derivatives showed a higher level of inhibition of DD-carboxypeptidase 64-575, a Penicillin Binding Protein (PBP), than the ferrocene derivatives and the reference compound penicillin G. Protein X-ray crystallographic analysis revealed a covalent acyl-enzyme complex of a ruthenocenyl compound with CTX-M β-lactamase E166A mutant, corresponding to a similar complex with PBPs responsible for the bactericidal activities of these compounds. Most interestingly, an intact compound was captured at the crystal-packing interface, elucidating for the first time the structure of a metallocenyl β-lactam compound that previously eluded small molecule crystallography. We propose that protein crystals, even from biologically unrelated molecules, can be utilized to determine structures of small molecules.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Medicine, University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, 12901 Bruce B. Downs Blvd., Tampa, Florida 33612, United States.