A cytosolic copper storage protein provides a second level of copper tolerance in Streptomyces lividans.
Straw, M.L., Chaplin, A.K., Hough, M.A., Paps, J., Bavro, V.N., Wilson, M.T., Vijgenboom, E., Worrall, J.A.R.(2018) Metallomics 10: 180-193
- PubMed: 29292456
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c7mt00299h
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6EI0, 6EK9 - PubMed Abstract:
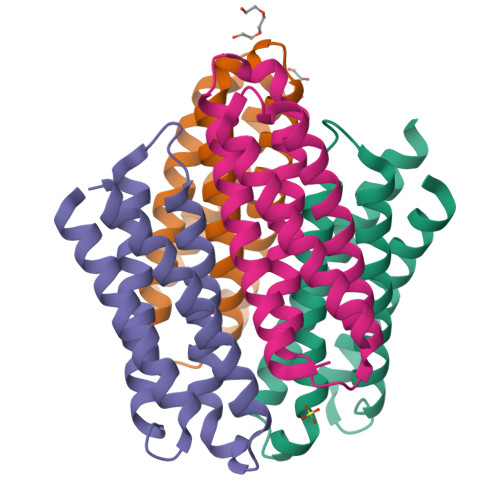
Streptomyces lividans has a distinct dependence on the bioavailability of copper for its morphological development. A cytosolic copper resistance system is operative in S. lividans that serves to preclude deleterious copper levels. This system comprises of several CopZ-like copper chaperones and P 1 -type ATPases, predominantly under the transcriptional control of a metalloregulator from the copper sensitive operon repressor (CsoR) family. In the present study, we discover a new layer of cytosolic copper resistance in S. lividans that involves a protein belonging to the newly discovered family of copper storage proteins, which we have named Ccsp (cytosolic copper storage protein). From an evolutionary perspective, we find Ccsp homologues to be widespread in Bacteria and extend through into Archaea and Eukaryota. Under copper stress Ccsp is upregulated and consists of a homotetramer assembly capable of binding up to 80 cuprous ions (20 per protomer). X-ray crystallography reveals 18 cysteines, 3 histidines and 1 aspartate are involved in cuprous ion coordination. Loading of cuprous ions to Ccsp is a cooperative process with a Hill coefficient of 1.9 and a CopZ-like copper chaperone can transfer copper to Ccsp. A Δccsp mutant strain indicates that Ccsp is not required under initial copper stress in S. lividans, but as the CsoR/CopZ/ATPase efflux system becomes saturated, Ccsp facilitates a second level of copper tolerance.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biological Sciences, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester, CO4 3SQ, UK. jworrall@essex.ac.uk.