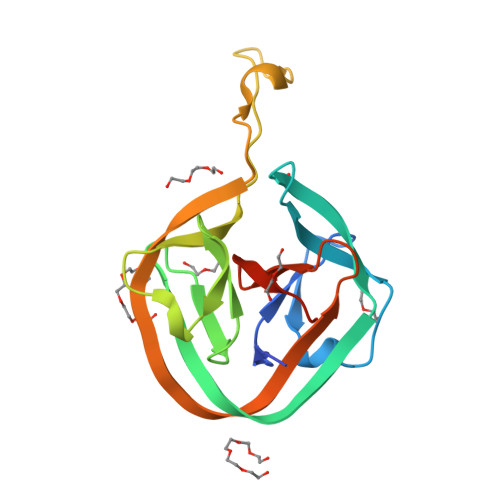
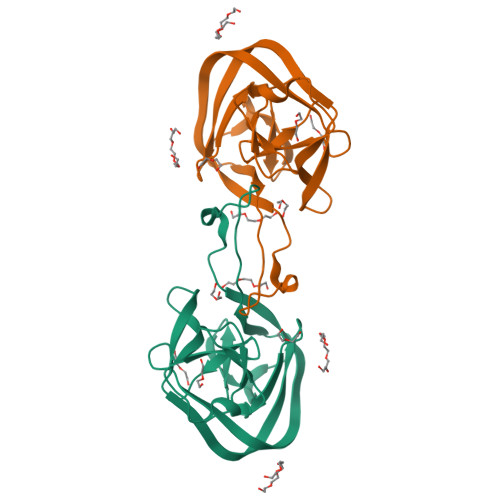
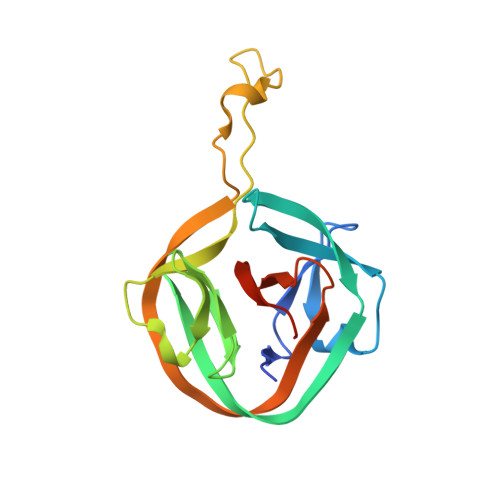
A functional interplay between intein and extein sequences in protein splicing compensates for the essential block B histidine.
Friedel, K., Popp, M.A., Matern, J.C.J., Gazdag, E.M., Thiel, I.V., Volkmann, G., Blankenfeldt, W., Mootz, H.D.(2019) Chem Sci 10: 239-251
- PubMed: 30713635
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c8sc01074a
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6FRE, 6FRG, 6FRH - PubMed Abstract:
Inteins remove themselves from a precursor protein by protein splicing. Due to the concomitant structural changes of the host protein, this self-processing reaction has enabled many applications in protein biotechnology and chemical biology. We show that the evolved M86 mutant of the Ssp DnaB intein displays a significantly improved tolerance towards non-native amino acids at the N-terminally flanking (-1) extein position compared to the parent intein, in the form of both an artificially trans -splicing split intein and the cis -splicing mini-intein. Surprisingly, side chains with increased steric bulk compared to the native Gly(-1) residue, including d-amino acids, were found to compensate for the essential block B histidine in His73Ala mutants in the initial N-S acyl shift of the protein splicing pathway. In the case of the M86 intein, large (-1) side chains can even rescue protein splicing activity as a whole. With the comparison of three crystal structures, namely of the M86 intein as well as of its Gly(-1)Phe and Gly(-1)Phe/His73Ala mutants, our data supports a model in which the intein's active site can exert a strain by varying mechanisms on the different angles of the scissile bond at the extein-intein junction to effect a ground-state destabilization. The compensatory mechanism of the block B histidine is the first example for the direct functional role of an extein residue in protein splicing. It sheds new light on the extein-intein interplay and on possible consequences of their co-evolution as well as on the laboratory engineering of improved inteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biochemistry , University of Muenster , Wilhelm-Klemm-Str. 2 , 48149 Münster , Germany . Email: Henning.Mootz@uni-muenster.de.